Scabies
What is Scabies ?
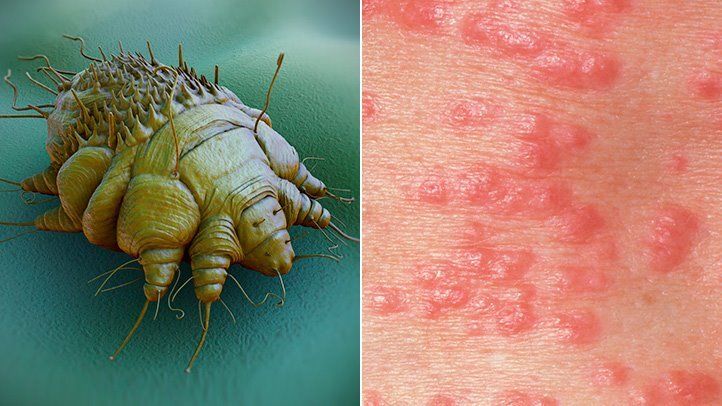
Scabies is an itchy skin rash caused by a tiny burrowing mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. Intense itching occurs in the area where the mite burrows. The need to scratch may be stronger at night. Scabies is contagious and can spread quickly through close person-to-person contact in a family, child care group, school class, nursing home, or prison.
Because scabies spreads so easily, health care providers often recommend treating the entire family or any close contacts. Scabies is easily treated. Medicated skin creams or pills kill the mites that cause scabies and their eggs. But itching may not stop for many weeks after treatment.
Symptoms
- Intense itching
- Pimple-like rash
- Visible burrows
- Sores from scratching
- Crusted scabies
- Rashes occur between fingers
- Rashes occur in the skin folds
- Rashes occur on the penis, nipples, waist, buttocks
- Burrowing tracks or bumps
- Thin, wavy tunnels made up of tiny blisters
Cause
Scabies is caused by a tiny, eight-legged mite. The female mite burrows just under the skin and makes a tunnel where it lays eggs. The eggs hatch, and the mite larvae travel to the surface of the skin, where they mature. These mites can then spread to other areas of the skin or the skin of other people. Itching is caused by the body’s allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs, and their waste. Close skin-to-skin contact and, less often, sharing clothing or bedding with a person who has scabies can spread the mites. Pets don’t spread scabies to humans. The scabies mites that affect animals don’t survive or reproduce in people. However, coming in contact with an animal that has scabies may cause brief itching if the mite gets under the skin. But within a few days, the mite will die. So treatment isn’t needed.
Risk Factors
Anyone can get scabies. It’s not a disease you get from poor hygiene. Some people are more likely to get scabies, including people who live in close, crowded conditions. Infants and children. (Children have a lot of close physical contact with their caregivers, friends, family members, and classmates.) People who are elderly, especially those living in nursing homes. Healthcare workers who care for people who aren’t aware they have scabies. Sexually active people. People with weak immune systems.
When to see a Doctor
Talk to your health care provider if you have any symptoms of scabies. Many skin conditions, such as dermatitis or eczema, can also cause itching and small bumps on the skin. Your health care provider can find the exact cause of your symptoms so that you receive the right treatment. Antihistamines or nonprescription lotions may ease itching. But they won’t get rid of the mites or their eggs.
