Pneumonia
What is Pneumonia ?
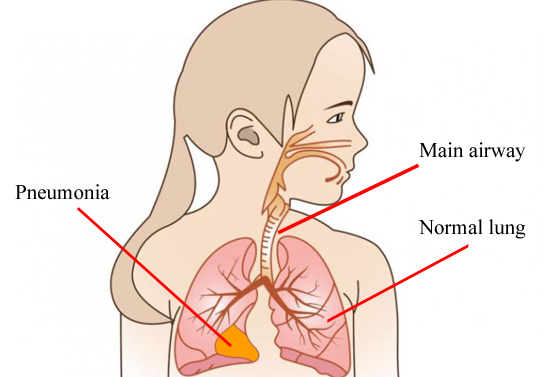
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Pneumonia can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening. It is most serious for infants and young children, people older than age 65, and people with health problems or weakened immune systems.
Symptoms
- High fever
- Cough with yellow, green or bloody mucus
- Tiredness
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating or chills
- Chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- Bluish skin, lips or nails (cyanosis)
- Confusion or altered mental state
- Dry cough
Cause
Pneumonia can develop when your immune system attacks an infection in the small sacs of your lung (alveoli). This causes your lungs to swell and leak fluids. Many bacteria, viruses and fungi can cause the infections that lead to pneumonia. Bacteria are the most common cause in adults and viruses are the most common cause in school-aged children. Common illnesses that can lead to pneumonia include Common cold (rhinovirus), COVID-19 (SARS-COV-2), The flu (influenza virus), Human metapneumovirus (HMPV), Human parainfluenza virus (HPIV), Legionnaires’ disease, Mycoplasma pneumonia bacteria, Pneumococcal disease, Pneumocystis pneumonia, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Risk Factors
Pneumonia can affect anyone. But the two age groups at highest risk are children who are 2 years old or younger and people who are age 65 or older. Other risk factors include Being hospitalized, You’re at greater risk of pneumonia if you’re in a hospital intensive care unit, especially if you’re on a machine that helps you breathe (a ventilator). Chronic disease, You’re more likely to get pneumonia if you have asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or heart disease. Smoking, Smoking damages your body’s natural defenses against the bacteria and viruses that cause pneumonia. Weakened or suppressed immune system, People who have HIV/AIDS, who’ve had an organ transplant, or who receive chemotherapy or long-term steroids are at risk.
When to see a Doctor
See your doctor if you have difficulty breathing, chest pain, persistent fever of 102 F (39 C) or higher, or persistent cough, especially if you’re coughing up pus.
