Meniere's Disease
What is Meniere's Disease ?
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear problem that can cause dizzy spells, also called vertigo, and hearing loss. Most of the time, Meniere’s disease affects only one ear.
Meniere’s disease can happen at any age. But it usually starts between the ages of 40 to 60. It’s thought to be a lifelong condition. But some treatments can help ease symptoms and lessen how it affects your life long term.
Symptoms
- Regular dizzy spells
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in the ear
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Vertigo
- Pressure
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Sweating
- Loss of balance
Cause
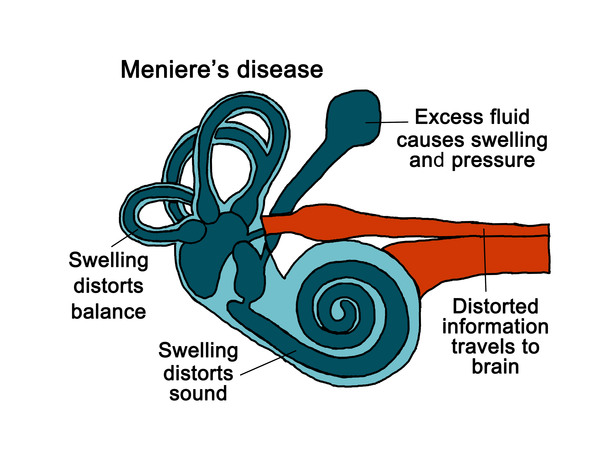
The cause of Meniere’s disease isn’t known. Symptoms of Meniere’s disease may be due to extra fluid in the inner ear called endolymph. But it isn’t clear what causes this fluid to build up in the inner ear. Issues that affect the fluid, which might lead to Meniere’s disease, include poor fluid drainage. This may be due to a blockage or irregular ear shape. Autoimmune disorders. Viral infection. Genetics. Because no single cause has been found, Meniere’s disease likely has a combination of causes.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include: Age. Ménière’s disease typically affects people ages 40 to 60. Sex. Some studies show that females are slightly more likely to develop this condition. Genes. About 7% to 10% of people with Ménière’s disease have a family history of the disorder. This means you may inherit the condition. Autoimmune diseases. You may be more likely to develop Ménière’s disease if you have an autoimmune disease. These include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and ankylosing spondylitis.
When to see a Doctor
See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of Meniere’s disease. Other illnesses can cause these problems. So, it’s important to find out what’s causing your symptoms as soon as possible.
