Male Infertility
What is Male Infertility ?
Nearly 1 in 7 couples is infertile, which means they haven’t been able to conceive a child even though they’ve had frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for a year or longer. In up to half of these couples, male infertility plays at least a partial role.
Male infertility can be caused by low sperm production, abnormal sperm function, or blockages that prevent the delivery of sperm. Illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices, and other factors may contribute to male infertility. The inability to conceive a child can be stressful and frustrating, but several treatments are available for male infertility.
Symptoms
- Difficulty with ejaculation
- Small volumes of fluid ejaculated
- Reduced sexual desire
- Difficulty maintaining an erection
- Pain, swelling or lump in testicle area
- Recurrent respiratory infections
- Inability to smell
- Abnormal breast growth
- Decreased facial or body hair
- A lower than normal sperm count
Cause
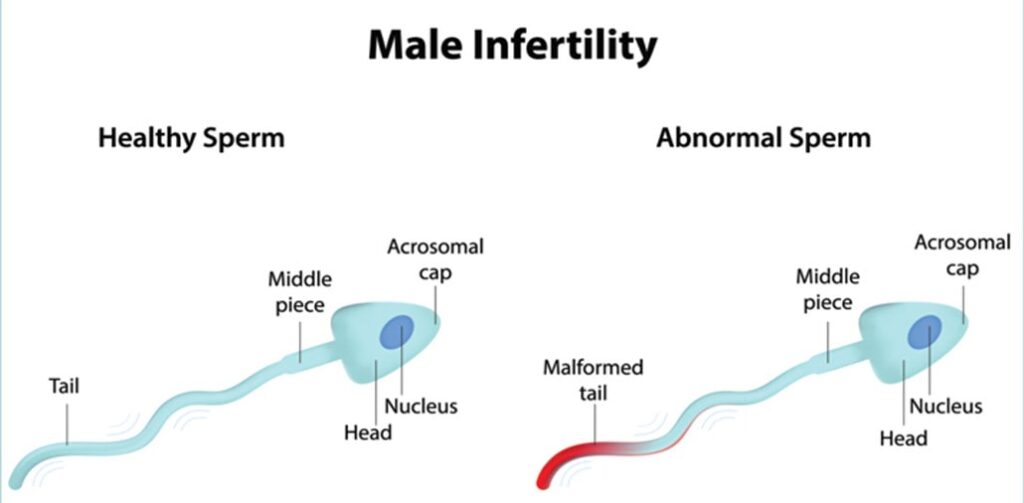
Male fertility is a complex process. To get your partner pregnant, the following must occur: You must produce healthy sperm. Initially, this involves the growth and formation of the male reproductive organs during puberty. At least one of your testicles must be functioning correctly, and your body must produce testosterone and other hormones to trigger and maintain sperm production. Sperm have to be carried into the semen. Once sperm are made in the testicles, delicate tubes transport them until they mix with semen and are ejaculated out of the penis. There needs to be enough sperm in the semen. If the number of sperm in your semen (sperm count) is low, it decreases the odds that one of your sperm will fertilize your partner’s egg. A low sperm count is fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen or fewer than 39 million per ejaculate. Sperm must be functional and able to move. If the movement (motility) or function of your sperm is abnormal, the sperm may not be able to reach or penetrate your partner’s egg.
Risk Factors
Risk factors linked to male infertility include smoking tobacco. Using alcohol. Using certain illicit drugs. Being overweight. Having certain past or present infections. Being exposed to toxins. Overheating the testicles. Having experienced trauma to the testicles. Having a prior vasectomy or major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Having a history of undescended testicles. Being born with a fertility disorder or having a blood relative with a fertility disorder. Having certain medical conditions, including tumors and chronic illnesses, such as sickle cell disease. Taking certain medications or undergoing medical treatments, such as surgery or radiation used for treating cancer.
When to see a Doctor
See a doctor if you have been unable to conceive a child after a year of regular, unprotected intercourse, or sooner if you have any of the following: Erection or ejaculation problems, low sex drive, or other issues with sexual function. Pain, discomfort, a lump, or swelling in the testicle area. A history of testicle, prostate, or sexual issues. A groin, testicle, penis or scrotum surgery. A partner over age 35.
