Kidney Cancer
What is Kidney Cancer ?
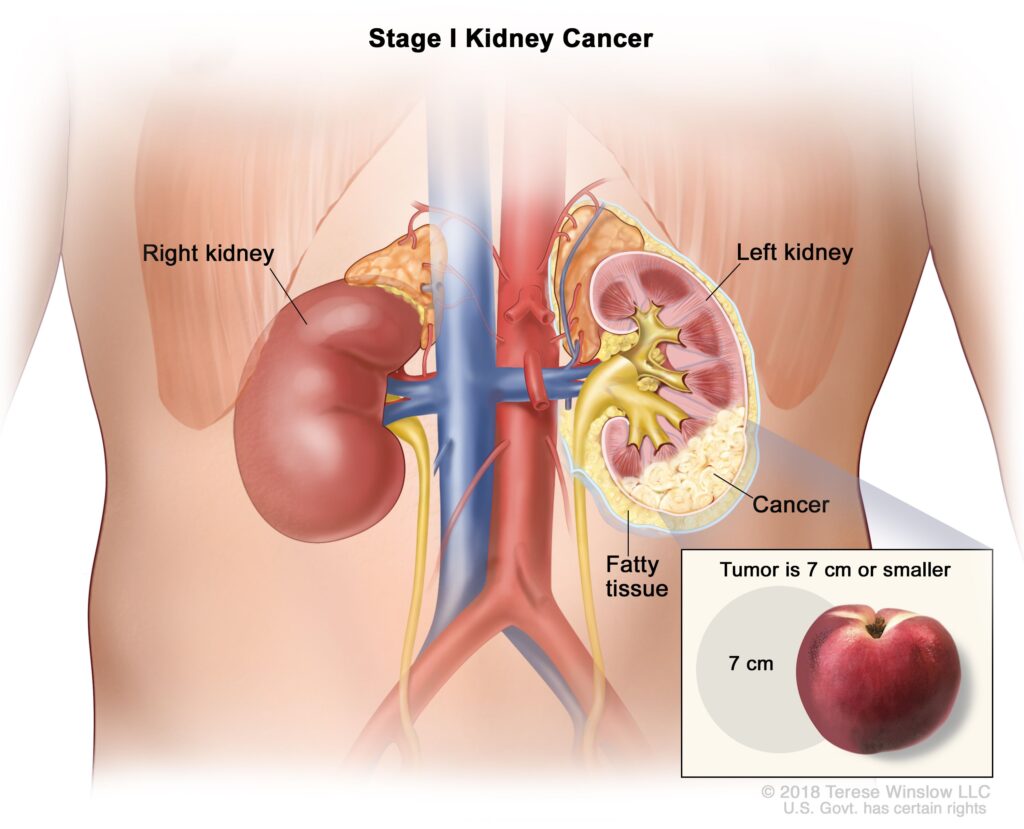
Kidney cancer is a growth of cells that starts in the kidneys. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They’re located behind the abdominal organs, with one kidney on each side of the spine. In adults, renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer. Other, less common types of kidney cancer can happen. Young children are more likely to develop a kind of kidney cancer called Wilms’ tumor.
The number of kidney cancers diagnosed each year seems to be increasing. One reason for this may be the fact that imaging techniques such as CT scans are being used more often. These tests may lead to the incidental discovery of more kidney cancers. Kidney cancer is often found when the cancer is small and confined to the kidney.
Symptoms
- Blood in your pee
- A lump or mass in your kidney area
- Flank pain
- Tiredness
- A general sense of not feeling well
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Low-grade fever
- Bone pain
- High blood pressure
- Anemia
- High calcium
Cause
It’s not clear what causes most kidney cancers. Kidney cancer happens when cells in the kidney develop changes in their DNA. A cell’s DNA holds the instructions that tell the cell what to do. In healthy cells, the DNA gives instructions to grow and multiply at a set rate. The instructions tell the cells to die at a set time. In cancer cells, the DNA changes give different instructions. The changes tell the cancer cells to make many more cells quickly. Cancer cells can keep living when healthy cells would die. This causes too many cells. The cancer cells form a mass called a tumor. The tumor can grow to invade and destroy healthy body tissue. In time, cancer cells can break away and spread to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads, it’s called metastatic cancer.
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of kidney cancer include: Older age. The risk of kidney cancer increases with age. Smoking tobacco. People who smoke have a greater risk of kidney cancer than those who don’t. The risk decreases after quitting. Obesity. People who are obese have a higher risk of kidney cancer than people who are considered to have a healthy weight. High blood pressure. High blood pressure, also called hypertension, increases the risk of kidney cancer. Certain inherited conditions. People who are born with certain inherited conditions may have an increased risk of kidney cancer. These conditions may include von Hippel-Lindau disease, Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, tuberous sclerosis complex, hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma, and familial renal cancer. Family history of kidney cancer. The risk of kidney cancer is higher if a blood relative, such as a parent or sibling, has had the disease.
When to see a Doctor
Make an appointment with a doctor or other healthcare professional if you have any symptoms that worry you.
