Hematuria
What is Hematuria ?
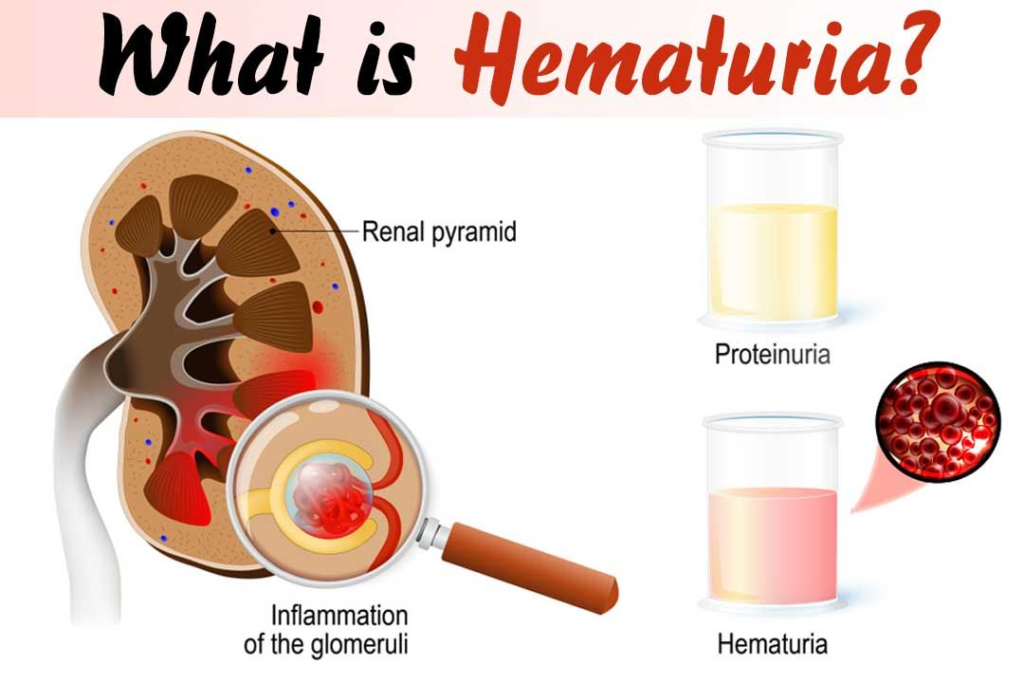
It can be scary to see blood in urine, also called hematuria. In many cases, the cause is harmless. But blood in the urine can also be a sign of a serious illness.
If you can see the blood, it’s called gross hematuria. Blood that can’t be seen with the naked eye is called microscopic hematuria. It’s such a small amount that it can be seen only under a microscope when a lab tests the urine. Either way, it’s important to figure out the reason for the bleeding. Treatment depends on the cause.
Symptoms
- Peeing more than usual
- Pain or burning when you pee
- A strong need to pee right away
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Chills
- Lower back pain
- Abdominal pain
- Pain on either side of your lower back
Cause
There are many different causes of hematuria. Some conditions are more serious than others. Serious conditions may include: Urinary stone disease. This term describes masses of minerals or other substances that form in your urinary system. This includes kidney stones, bladder stones, and ureteral stones. Urinary tract infection (UTI). This is a bacterial infection in any part of your urinary system. Kidney infection (pyelonephritis). This is an infection that spreads to your kidney(s). Bladder inflammation (cystitis). This is when inflammation affects your urinary bladder. It may have infectious or noninfectious causes. Certain cancers can also cause blood to appear in your urine. Other conditions that may lead to blood in your pee include an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hypertrophy or BPH). BPH causes your prostate to grow. Your prostate is a gland that produces semen. Injury to your urinary system. Examples include blunt trauma (like a fall, automobile collision, or sports injury) or a penetrating injury (like a knife wound or gunshot wound). Menstruation. You may see blood in your pee when you have your period. Endometriosis. This causes tissue that’s similar to your uterine lining (where blood and tissue come from during menstruation) to grow outside of your uterus. Chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD affects how well your kidneys work. It’s a long-term (chronic) condition. Sickle cell disease. This is a condition you inherit from your biological parents that affects your red blood cells.
Risk Factors
Almost anyone can have red blood cells in the urine. This includes children and teens. Some things that can raise the risk of blood in the urine include: Age. Middle-aged and older men may be more likely to have hematuria due to an enlarged prostate gland. The risk of some cancers that can cause blood in the urine may also rise after the age of 50. Urinary tract infection. This is one of the top causes of blood that can be seen in children’s urine. Family history. The chances of having blood in the urine may go up if one or more family members have had kidney disease. Certain medicines. Some pain relievers, blood thinners, and antibiotics can raise the risk of blood in the urine. Hard exercise. Marathon runner’s hematuria is one nickname for hematuria. Contact sports can raise the risk, too.
When to see a Doctor
See a health care provider whenever urine looks like it might have blood in it. Red urine isn’t always caused by red blood cells. Some medicines can cause urine to turn red, such as a medicine called phenazopyridine that eases urinary tract symptoms. Certain foods can also turn urine red, including beets and rhubarb. It can be hard to tell whether a change in urine color is caused by blood. That’s why it’s always best to get a checkup.
