Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease ?
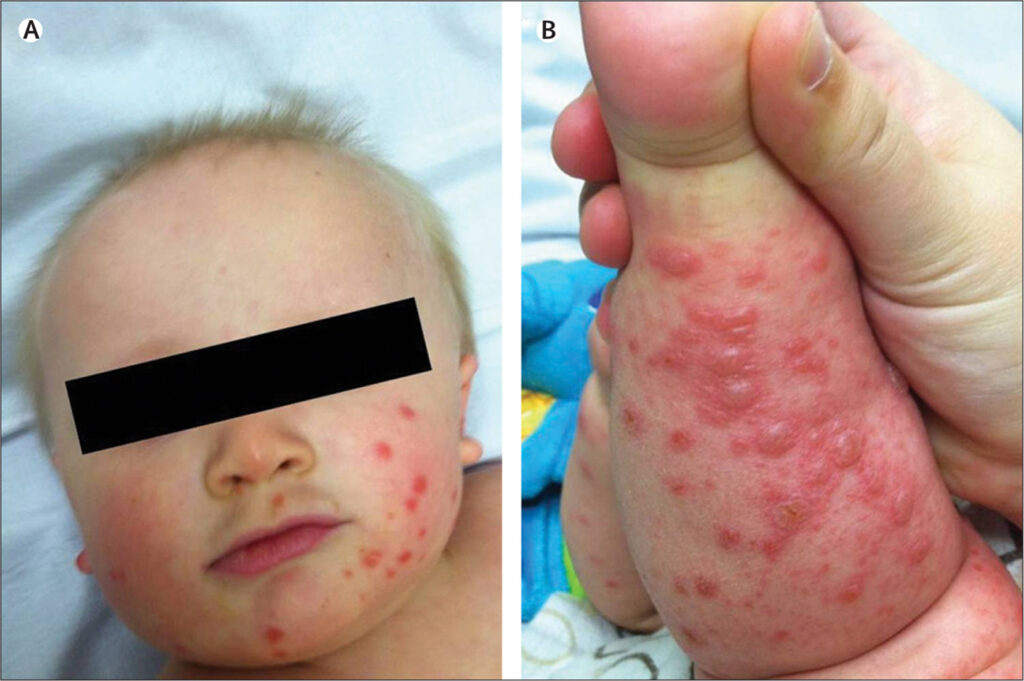
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a mild, contagious viral infection common in young children. Symptoms include sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet. Hand, foot, and mouth disease is most commonly caused by a coxsackievirus.
There’s no specific treatment for hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with people who have hand, foot, and mouth disease may help lower your child’s risk of infection.
Symptoms
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Feeling sick
- Painful, blister-like lesions
- Rash
- Headache
- Fussiness in infants and toddlers
- Loss of appetite
- Runny nose
- Stomachache
- Painful mouth sores
- Swollen lymph nodes in their neck
Cause
The most common cause of hand-foot-and-mouth disease is infection from coxsackievirus 16. This coxsackievirus belongs to a group of viruses called nonpolio enteroviruses. Other types of enteroviruses may also cause hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Most people get the coxsackievirus infection — and hand-foot-and-mouth disease — through the mouth. The illness spreads by person-to-person contact with an infected person’s nose secretions or throat discharge, saliva, fluid from blisters, stool, or respiratory droplets sprayed into the air after a cough or sneeze. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most common in children in child care. That’s because young children need frequent diaper changes and help using the toilet. They also tend to put their hands in their mouths. Your child is most contagious during the first week of having hand-foot-and-mouth disease. But the virus can remain in the body for weeks after the symptoms go away. That means your child can still infect others. Some people, especially adults, can pass the virus without showing any symptoms of the disease. Outbreaks of the disease are more common in summer and early autumn in the United States. In tropical climates, outbreaks occur during the rainy season.
Risk Factors
Age is the main risk factor for hand-foot-and-mouth disease. The disease mostly affects children younger than the ages of 5 to 7 years old. Children in child care settings are especially vulnerable because the infection spreads by person-to-person contact. Hand-foot-mouth disease typically affects young children, but anyone can get it. Older children and adults are thought to have immunity against hand-foot-and-mouth disease. They often build antibodies after exposure to the viruses that cause the disease. But adolescents and adults sometimes still get hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
When to see a Doctor
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is usually a minor illness. It typically only causes fever and mild symptoms for a few days. Call your health care provider if your child is younger than six months, has a weakened immune system, or has mouth sores or a sore throat that makes it painful to drink fluids. Call your provider, too, if your child’s symptoms don’t improve after 10 days.
