Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production and wheezing. It’s typically caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. People with COPD are at increased risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer and a variety of other conditions.
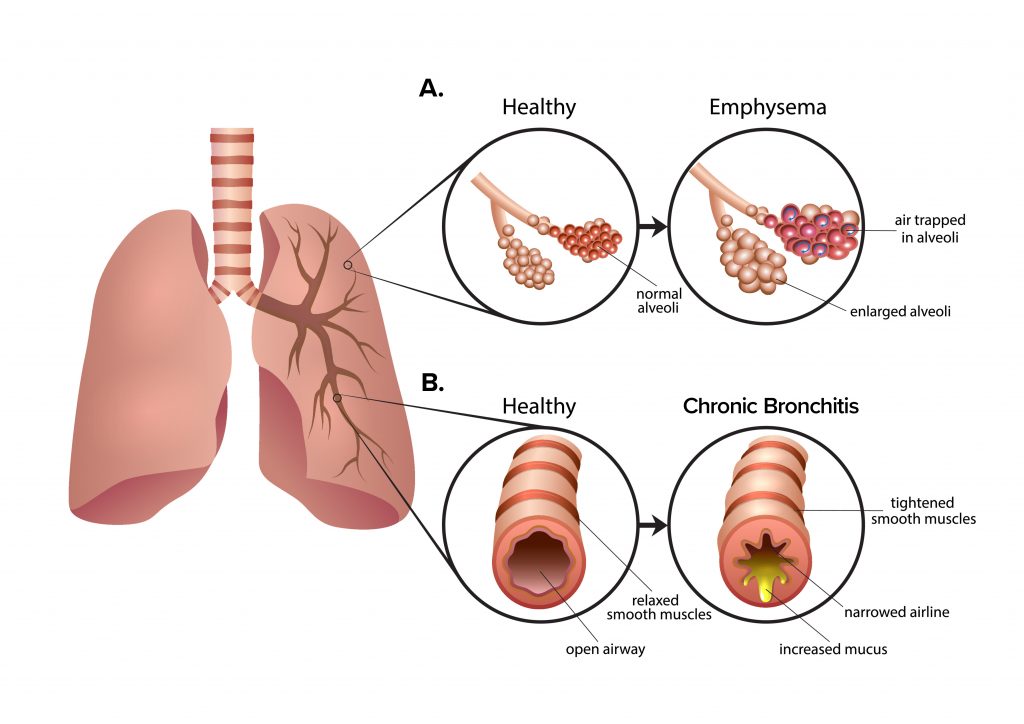
Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two most common conditions that contribute to COPD. These two conditions usually occur together and can vary in severity among individuals with COPD. Chronic bronchitis is inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. It’s characterized by daily cough and mucus (sputum) production.
Emphysema is a condition in which the alveoli at the end of the smallest air passages (bronchioles) of the lungs are destroyed as a result of damaging exposure to cigarette smoke and other irritating gases and particulate matter. Although COPD is a progressive disease that gets worse over time, COPD is treatable. With proper management, most people with COPD can achieve good symptom control and quality of life, as well as reduced risk of other associated conditions.
Symptoms
- Trouble catching your breath
- Wheezing or whistling sounds when breathing
- Ongoing cough that may bring up a lot of mucus
- Chest tightness or heaviness
- Lack of energy or feeling very tired
- Frequent lung infections
- Losing weight without meaning to
- Swelling in ankles, feet or legs
- Coughing more often
- Fever
Cause
The main cause of COPD in developed countries is tobacco smoking. In the developing world, COPD often occurs in people exposed to fumes from burning fuel for cooking and heating in homes that don’t have good airflow. Long-term exposure to chemical fumes, vapors and dusts in the workplace is another cause of COPD. Not all people who have smoked for a long time have COPD symptoms, but they may still have lung damage, so their lungs don’t work as well as they used to. Some people who smoke get less common lung conditions that may be diagnosed as COPD until a more thorough exam shows a different diagnosis.
Risk Factors
While smoking is the biggest risk factor for COPD, not everyone who smokes will develop it. You may be at higher risk for COPD if you are female, are over the age of 65, have been exposed to air pollution, have worked with chemicals, dust or fumes, have alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, had many respiratory infections during childhood.
When to see a Doctor
Talk with your doctor or other healthcare professional if your symptoms don’t get better with treatment or if symptoms get worse. Also talk with your healthcare professional if you notice symptoms of an infection, such as fever or a change in the mucus you cough up. Call your local emergency number for help or go to the emergency department at a hospital right away if you can’t catch your breath, your lips or fingernail beds are blue, you have a fast heartbeat, or you feel foggy and have trouble concentrating.
