Patients
- Upload Prescription
- Request A Call Back
- Book A Test
- Download Report
- TRF For COVID-19
- Feedback
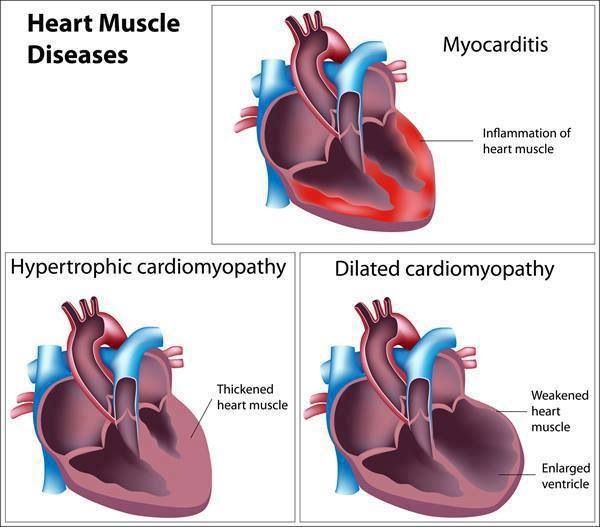
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that usually starts in your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle). The ventricle stretches and thins (dilates) and can’t pump blood as well as a healthy heart can. Over time, both ventricles may be affected. The term “cardiomyopathy” refers to diseases that affect the heart muscle itself.
Dilated cardiomyopathy might not cause symptoms, but for some people it can be life-threatening. It’s a common cause of heart failure. Dilated cardiomyopathy can also lead to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), blood clots or sudden death. The condition can affect anyone, including infants and children.
If a family member has dilated cardiomyopathy, talk to your doctor. Early detection using genetic testing may benefit people with inherited forms of dilated cardiomyopathy who have no apparent signs or symptoms.
a division of exult cares pvt. ltd.