Gynaecological Cancer
What is Gynaecological Cancer ?
Gynaecological cancer is a term used for all the types of cancer that can occur in or on a woman’s reproductive organs and genitals. This includes cancers of the vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. About 9.7% of all cancers diagnosed in Australian women are gynaecological cancers.
While there are screening tests for some gynaecological cancers, for others there is no proven screening method. This means that it’s important for women to be aware of the possible signs and symptoms of gynaecological cancers and get to know their bodies well, so they can tell if anything changes. Below, we’ve listed the different types of gynaecological cancers, their symptoms, possible methods of prevention and applicable screening programs.
Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Fleeing full too quickly or difficulty eating
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- More frequent r urgent need to urinate
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Abdominal or back pain
- Itching, burning, pain of the vulva
- Changes in vulva color of skin
- Abdominal swelling
Cause
Gynecologic cancers, which affect a woman’s reproductive organs, can be caused by various factors, including HPV infection, smoking, obesity, family history, and certain genetic predispositions. Such as, persistent HPV infection is the primary cause of cervical cancer, with nearly all cases linked to HPV. Smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of HPV infections lasting longer, potentially leading to cervical cancer. Other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can increase the risk of HPV infection, which can then lead to cervical cancer.
Risk Factors
Gynecologic cancer risk factors include family history, obesity, age, HPV infection, and certain genetic mutations, but also lifestyle factors like smoking and diet. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of common risk factors for gynecologic cancers : Age, Family History, Obesity, Smoking, Hormone Replacement Therapy, Genetic Mutations, Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection, Reproductive History, Diabetes, Certain Medical Conditions.
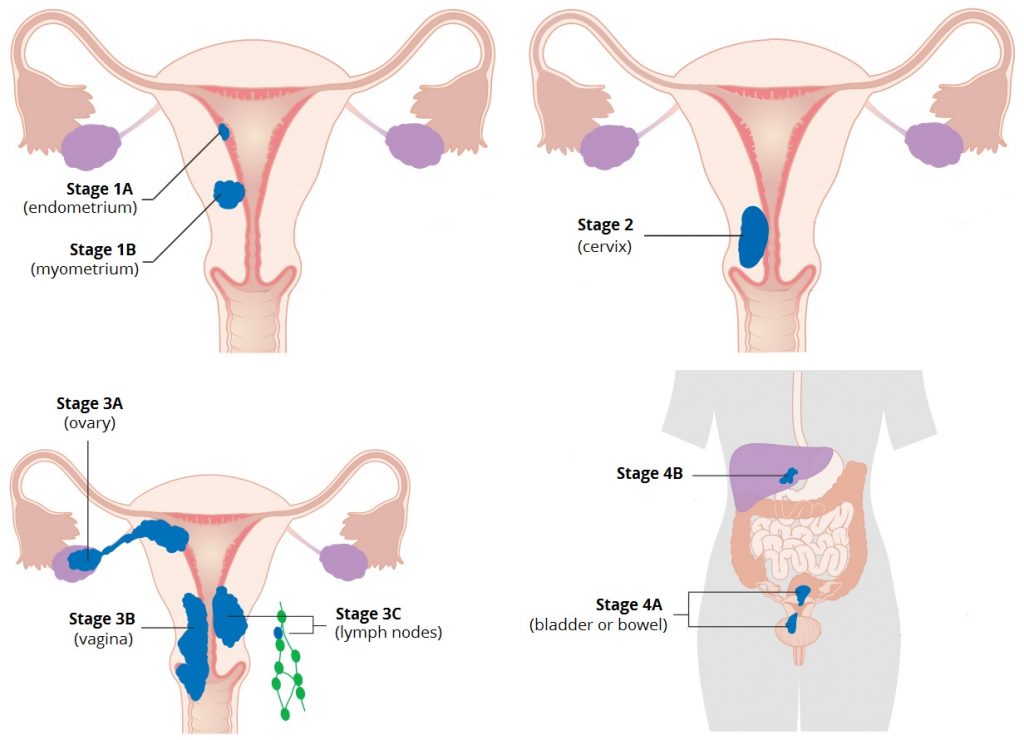
When to see a Doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If you have a family history of gynaecological cancer, talk to your doctor about your risk. Your doctor may refer you to a genetic counselor to discuss testing for certain gene mutations that increase your risk of gynaecological cancers.
References : 1. Google
