Head Injury
What is Head Injury ?
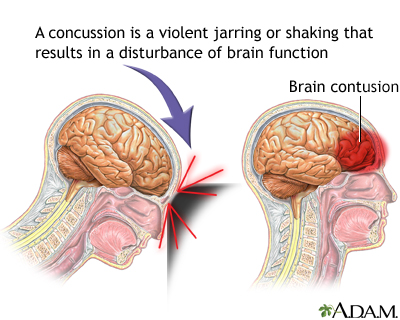
Traumatic brain injury usually results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body. An object that goes through brain tissue, such as a bullet or shattered piece of skull, also can cause traumatic brain injury.
Mild traumatic brain injury may affect your brain cells temporarily. More-serious traumatic brain injury can result in bruising, torn tissues, bleeding and other physical damage to the brain. These injuries can result in long-term complications or death.
Symptoms
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Problems with speech
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sensory problems
- Loss of consciousness for a few seconds
- No loss of consciousness
- Memory or concentration problems
- Mood changes or mood swings
- Feeling depressed or anxious
- Difficulty sleeping
Cause
Traumatic brain injury is usually caused by a blow or other traumatic injury to the head or body. The degree of damage can depend on several factors, including the nature of the injury and the force of impact. Common events causing traumatic brain injury include the following, Falls. Falls from bed or a ladder, down stairs, in the bath, and other falls are the most common cause of traumatic brain injury overall, particularly in older adults and young children. Vehicle-related collisions. Collisions involving cars, motorcycles or bicycles — and pedestrians involved in such accidents — are a common cause of traumatic brain injury. Violence. Gunshot wounds, domestic violence, child abuse and other assaults are common causes. Shaken baby syndrome is a traumatic brain injury in infants caused by violent shaking. Sports injuries. Traumatic brain injuries may be caused by injuries from a number of sports, including soccer, boxing, football, baseball, lacrosse, skateboarding, hockey, and other high-impact or extreme sports. These are particularly common in youth. Explosive blasts and other combat injuries. Explosive blasts are a common cause of traumatic brain injury in active-duty military personnel. Although how the damage occurs isn’t yet well understood, many researchers believe that the pressure wave passing through the brain significantly disrupts brain function. Traumatic brain injury also results from penetrating wounds, severe blows to the head with shrapnel or debris, and falls or bodily collisions with objects following a blast.
Risk Factors
The people most at risk of traumatic brain injury include children, especially newborns to 4-year-olds. Young adults, especially those between ages 15 and 24. Adults age 60 and older. Males in any age group.
When to see a Doctor
Always see your doctor if you or your child has received a blow to the head or body that concerns you or causes behavioral changes. Seek emergency medical care if there are any signs or symptoms of traumatic brain injury following a recent blow or other traumatic injury to the head. The terms “mild,” “moderate” and “severe” are used to describe the effect of the injury on brain function. A mild injury to the brain is still a serious injury that requires prompt attention and an accurate diagnosis.
