Athlete's Foot
What is Athlete's Foot ?
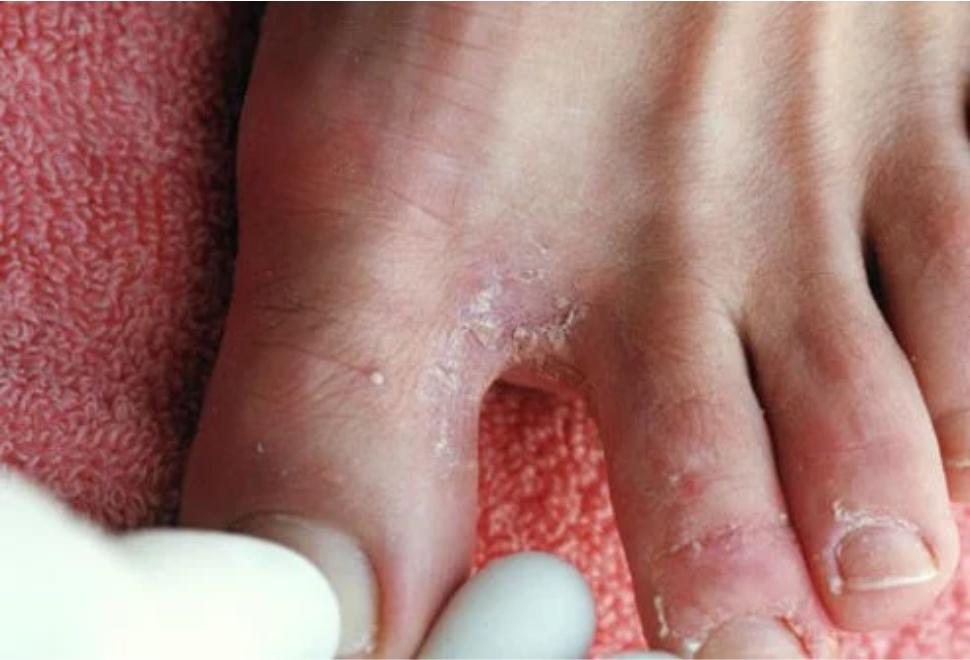
Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is a fungal skin infection that usually begins between the toes. It commonly occurs in people whose feet have become very sweaty while confined within tight-fitting shoes.
Signs and symptoms of athlete’s foot include an itchy, scaly rash. The condition is contagious and can be spread via contaminated floors, towels or clothing. Athlete’s foot is closely related to other fungal infections such as ringworm and jock itch. It can be treated with antifungal medications, but the infection often comes back.
Symptoms
- Scaly, peeling or cracked skin between the toes
- Itchiness
- Inflamed skin
- Burning
- Blisters
- Dry, scaly skin on the bottom of the foot
- Peeling skin
- A skin rash
- Stinging
- Thickened skin
Cause
Athlete’s foot is caused by the same type of fungi (dermatophytes) that cause ringworm and jock itch. Damp socks and shoes and warm, humid conditions favor the organisms’ growth. Athlete’s foot is contagious and can spread through contact with an infected person or from contact with contaminated surfaces, such as towels, floors and shoes. You can also spread it from the foot to other parts of the body, especially if you scratch or pick the infected parts of your foot.
Risk Factors
You are at higher risk of athlete’s foot if you frequently wear enclosed footwear. Sweat heavily. Share mats, rugs, bed linens, clothes or shoes with someone who has a fungal infection. Walk barefoot in public areas where the infection can spread, such as locker rooms, saunas, swimming pools, communal baths and showers.
When to see a Doctor
If you have a rash on your foot that doesn’t improve within two weeks of beginning self-treatment with an over-the-counter antifungal product, see your doctor. If you have diabetes, see your doctor if you suspect that you have athlete’s foot. Also see your doctor if you have signs of an infection — swelling of the affected area, pus, fever.
