Acne
What is Acne ?
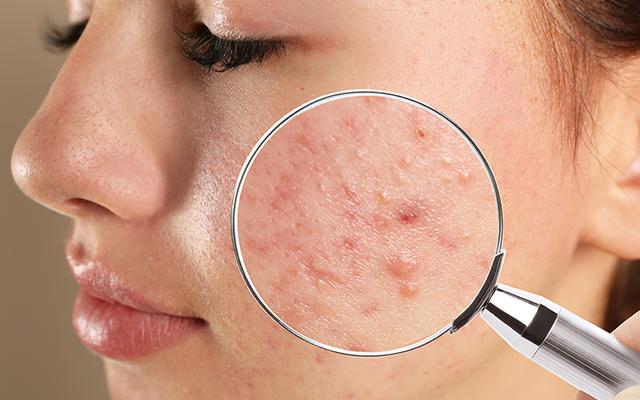
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when your hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells. It causes whiteheads, blackheads or pimples. Acne is most common among teenagers, though it affects people of all ages.
Effective acne treatments are available, but acne can be persistent. The pimples and bumps heal slowly, and when one begins to go away, others seem to crop up. Depending on its severity, acne can cause emotional distress and scar the skin. The earlier you start treatment, the lower your risk of such problems.
Symptoms
- Whiteheads
- Blackheads
- Small red, tender bumps
- Pimples
- Large, solid, painful lumps under the skin
- Painful, pus-filled lumps under the skin
- Nodules
- Cysts
- Scarring
- Redness and Inflammation
Cause
Four main factors cause acne: excessive oil (sebum) production. Hair follicles are clogged by oil and dead skin cells. Bacteria. Inflammation. Certain things may trigger or worsen acne, hormonal changes. Androgens are hormones that increase in boys and girls during puberty and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and make more sebum. Hormone changes during midlife, particularly in women, can lead to breakouts, too. Certain medications. Examples include drugs containing corticosteroids, testosterone, or lithium. Diet. Studies indicate that consuming certain foods — including carbohydrate-rich foods such as bread, bagels, and chips — may worsen acne. Further study is needed to examine whether people with acne would benefit from following specific dietary restrictions. Stress. Stress doesn’t cause acne, but if you have acne already, stress may make it worse.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for acne include Age. People of all ages can get acne, but it’s most common in teenagers. Hormonal changes. Such changes are common during puberty or pregnancy. Family history. Genetics plays a role in acne. If both of your parents had acne, you’re likely to develop it too. Greasy or oily substances. You may develop acne where your skin comes into contact with oil or oily lotions and creams. Friction or pressure on your skin. This can be caused by items such as telephones, cellphones, helmets, tight collars, and backpacks.
When to see a Doctor
If self-care remedies don’t clear your acne, see your primary care doctor. He or she can prescribe stronger medications. If acne persists or is severe, you may want to seek medical treatment from a doctor who specializes in the skin (dermatologist or pediatric dermatologist).
