Vaginitis
What is Vaginitis ?
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching and pain. The cause is usually a change in the balance of vaginal bacteria or an infection. Reduced estrogen levels after menopause and some skin disorders also can cause vaginitis.
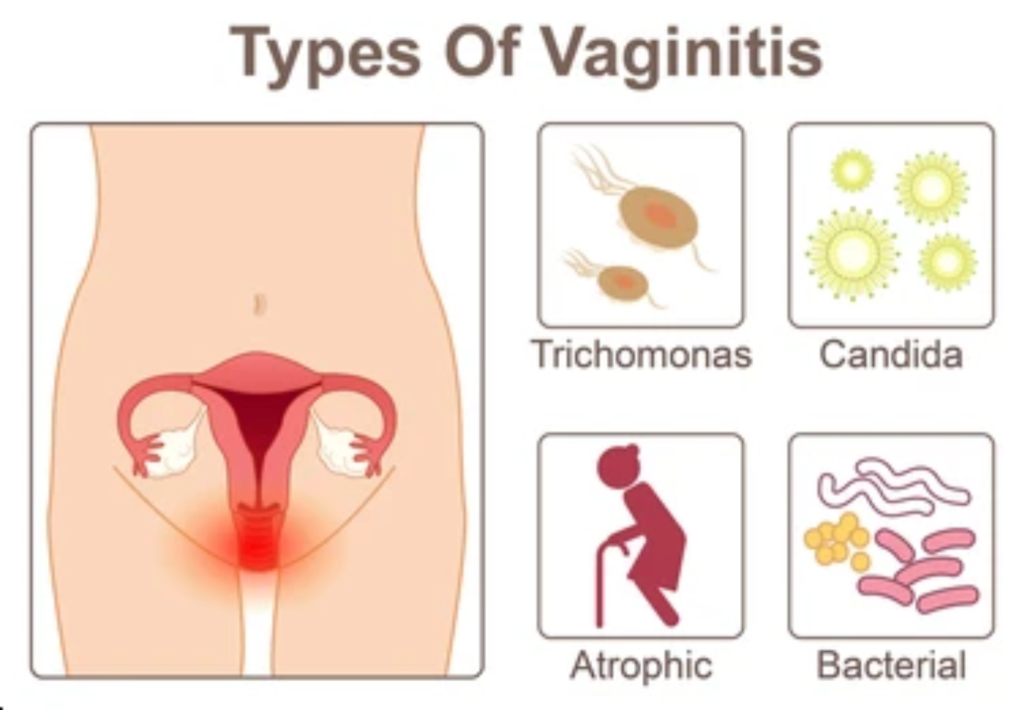
The most common types of vaginitis are:
- Bacterial vaginosis. This results from an overgrowth of the bacteria naturally found in your vagina, which upsets the natural balance.
- Yeast infections. These are usually caused by a naturally occurring fungus called Candida albicans.
- Trichomoniasis. This is caused by a parasite and is often sexually transmitted.
Treatment depends on the type of vaginitis you have.
Symptoms
- Change in color, odor or amount of discharge
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- Pain during sex
- Painful urination
- Light vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Vaginal burning
- Your vulva may even feel swollen
- Vaginal dryness
- Cracked skin around your vagina
- Redness around the opening to the vagina
Cause
The cause depends on what type of vaginitis you have Bacterial vaginosis. This most common type of vaginitis results from a change of the bacteria found in your vagina, upsetting the balance. What causes the imbalance is unknown. It’s possible to have bacterial vaginosis without symptoms. Yeast infections. These occur when there’s an overgrowth of a fungal organism — usually Candida albicans — in your vagina. C. albicans also causes infections in other moist areas of your body, such as in your mouth (thrush), skin folds and nail beds. The fungus can also cause diaper rash. Trichomoniasis. This common sexually transmitted infection is caused by a microscopic, one-celled parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. This organism spreads during sex with someone who has the infection. Noninfectious vaginitis. Vaginal sprays, douches, perfumed soaps, scented detergents and spermicidal products can cause an allergic reaction or irritate vulvar and vaginal tissues. Foreign objects, such as toilet paper or forgotten tampons, in the vagina also can irritate vaginal tissues.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing vaginitis include Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy, birth control pills or menopause. Sexual activity. Having a sexually transmitted infection. Medications, such as antibiotics and steroids. Use of spermicides for birth control. Uncontrolled diabetes. Use of hygiene products such as bubble bath, vaginal spray or vaginal deodorant. Douching. Wearing damp or tight-fitting clothing. Using an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control.
When to see a Doctor
See your doctor if you develop unusual vaginal discomfort.
