Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
What is Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura ?
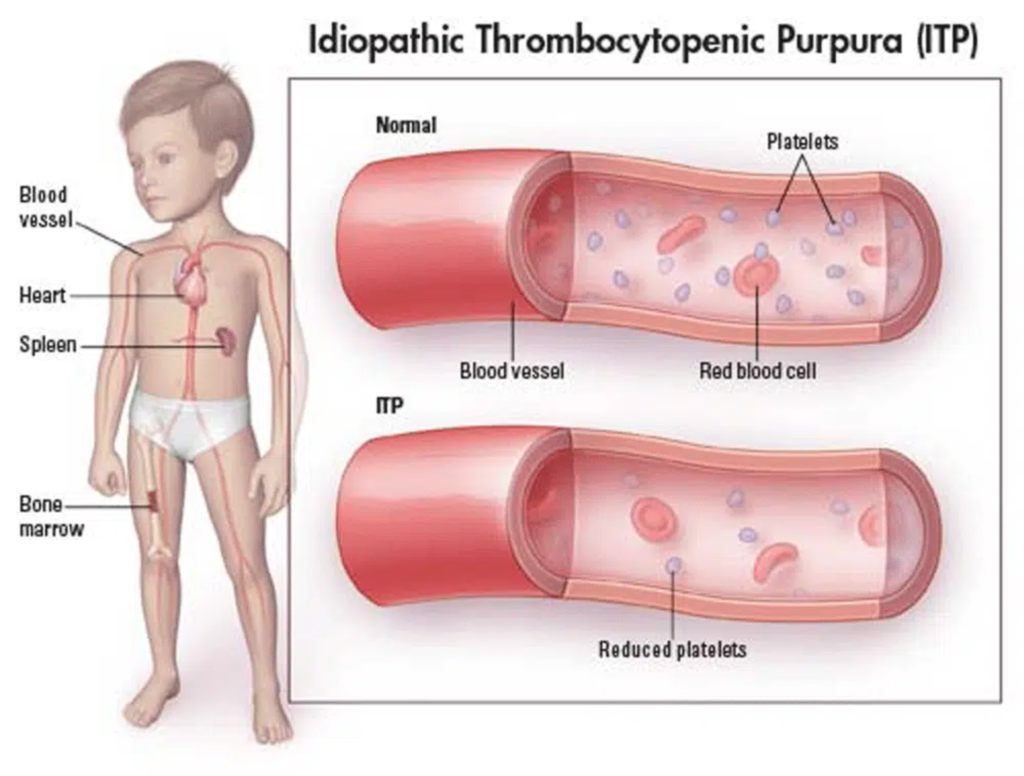
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an illness that can lead to bruising and bleeding. Low levels of the cells that help blood clot, also known as platelets, most often cause the bleeding. Once known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, ITP can cause purple bruises. It can also cause tiny reddish-purple dots on the skin that look like a rash.
Children can get ITP after a virus. They most often get better without treatment. In adults, the illness often lasts months or years. People with ITP who aren’t bleeding and whose platelet count isn’t too low might not need treatment. For worse symptoms, treatment might include medicines to raise the platelet count or surgery to remove the spleen.
Symptoms
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding into the skin
- Bleeding from the gums or nose
- Blood in urine or stools
- Really heavy menstrual flow
- Purpura
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Hematoma
- Fatigue
- Internal Bleeding
Cause
Immune thrombocytopenia usually happens when the immune system makes a mistake. It attacks and destroys the cells that help blood clot, also known as platelets.
In adults, an infection with HIV, hepatitis or the bacteria that causes stomach ulcers, known as H. pylori, can cause ITP. In most children with ITP, the disorder follows a virus, such as the mumps or the flu.
Risk Factors
ITP is more common among young women. The risk appears to be higher in people who also have other diseases in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
When to see a Doctor
Make an appointment with your health care provider if you or your child has symptoms that worry you. Bleeding that won’t stop is a medical emergency. Seek help right away if you or your child has bleeding that the usual first aid efforts can’t control. These include applying pressure to the area.
