Iron Deficiency Anemia
What is Iron Deficiency Anemia ?
Iron deficiency anemia is a common type of anemia — a condition in which blood lacks adequate healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. As the name implies, iron deficiency anemia is due to insufficient iron. Without enough iron, your body can’t produce enough of a substance in red blood cells that enables them to carry oxygen (hemoglobin). As a result, iron deficiency anemia may leave you tired and short of breath.
You can usually correct iron deficiency anemia with iron supplementation. Sometimes additional tests or treatments for iron deficiency anemia are necessary, especially if your doctor suspects that you’re bleeding internally.
Symptoms
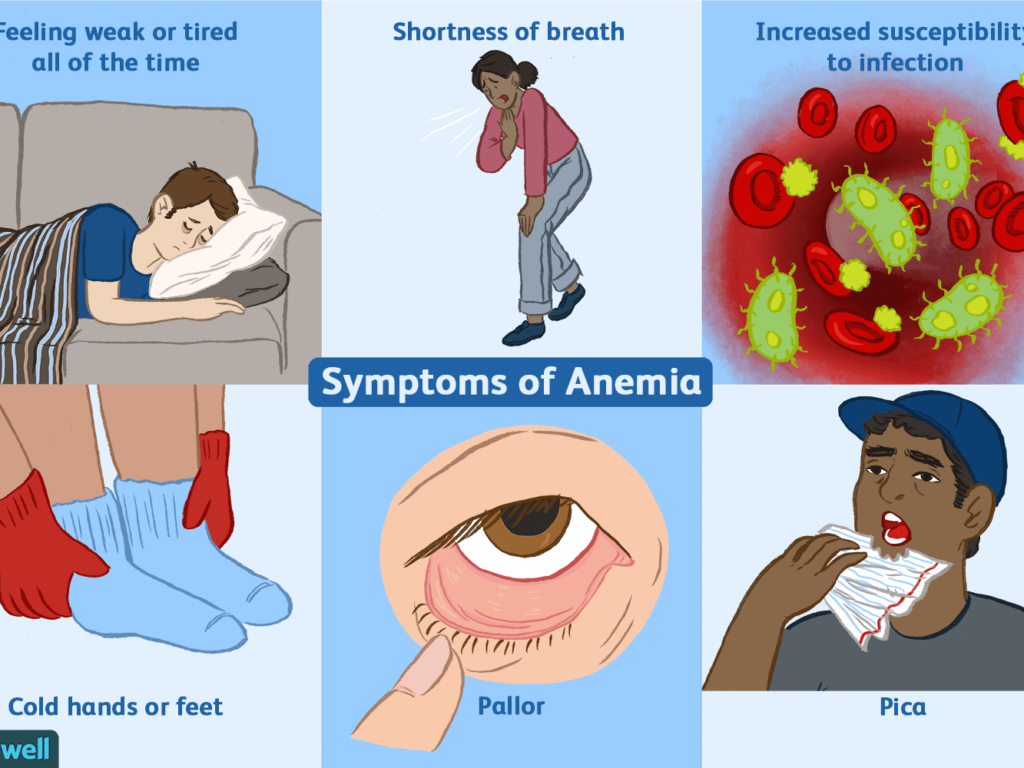
- Extreme fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale skin
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Cold hands and feet
- Inflammation
- Brittle nails
- Unusual cravings for non-nutritive substances
- Poor appetite
Cause
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when your body doesn’t have enough iron to produce hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the part of red blood cells that gives blood its red color and enables the red blood cells to carry oxygenated blood throughout your body. If you aren’t consuming enough iron, or if you’re losing too much iron, your body can’t produce enough hemoglobin, and iron deficiency anemia will eventually develop. Causes of iron deficiency anemia include Blood loss, A lack of iron in your diet, An inability to absorb iron, Pregnancy.
Risk Factors
These groups of people may have an increased risk of iron deficiency anemia : Women. Because women lose blood during menstruation, women in general are at greater risk of iron deficiency anemia. Infants and children. Infants, especially those who were low birth weight or born prematurely, who don’t get enough iron from breast milk or formula may be at risk of iron deficiency. Children need extra iron during growth spurts. If your child isn’t eating a healthy, varied diet, he or she may be at risk of anemia. Vegetarians. People who don’t eat meat may have a greater risk of iron deficiency anemia if they don’t eat other iron-rich foods. Frequent blood donors. People who routinely donate blood may have an increased risk of iron deficiency anemia since blood donation can deplete iron stores. Low hemoglobin related to blood donation may be a temporary problem remedied by eating more iron-rich foods. If you’re told that you can’t donate blood because of low hemoglobin, ask your doctor whether you should be concerned.
When to see a Doctor
If you or your child develops signs and symptoms that suggest iron deficiency anemia, see your doctor. Iron deficiency anemia isn’t something to self-diagnose or treat. So, see your doctor for a diagnosis rather than taking iron supplements on your own. Overloading the body with iron can be dangerous because excess iron accumulation can damage the liver and cause other complications.
