Acromegaly
What is Acromegaly ?
Acromegaly is a rare condition in adults that causes some bones, organs and other tissue to grow bigger. A small gland in the brain called the pituitary gland drives these changes by making too much growth hormone. This usually happens due to a tumor of the pituitary gland. The tumor isn’t cancer. When the body has too much growth hormone, bones get bigger. In childhood, this leads to increased height as part of a condition called gigantism. In adults with acromegaly, a change in height doesn’t happen. Instead, bones in the hands, feet and face become bigger.
These changes happen slowly over many years. So people with acromegaly and their loved ones may take a long time to notice the symptoms. And healthcare professionals may have a hard time finding and treating the condition early on.Without treatment, acromegaly can lead to other serious and sometimes life-threatening health conditions called complications. But treatments such as surgery, medicine and radiation can lower the risk of complications. Treatment also can improve many acromegaly symptoms.
Symptoms
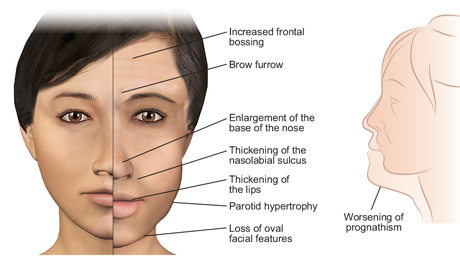
- Enlarged hands or feet
- Changes in your face shape
- Increase in size of your lips, nose and/or tongue
- Excessive sweating or oily skin
- Deepening of your voice
- Headaches
- Joint pain
- Vision changes
- Increase in the number of skin tags
- Numbness in your hands
- Sleep apnea
- Carpal tunnel syndrome or spinal cord issues
Cause
The most common cause of acromegaly is a tumor in the pituitary gland. The tumor is called an adenoma. It isn’t cancer. But it makes too much growth hormone over a long amount of time. Too much growth hormone causes many symptoms of acromegaly. Some of the symptoms, such as headaches and impaired vision, are due to the tumor pressing on nearby brain tissues. Rarely, tumors in other parts of the body cause acromegaly. These include tumors of the lung or pancreas. Sometimes these tumors release growth hormone. Or they make a hormone called growth hormone-releasing hormone. This signals the pituitary gland to make more growth hormone. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, behind the bridge of the nose. It makes growth hormone and other hormones. Growth hormone plays an important role in controlling physical growth. The pituitary gland releases growth hormone into the bloodstream. This triggers the liver to make a hormone called insulin-like growth factor-1, also called IGF-1. IGF-1 is really what causes bones and other tissues to grow. Too much growth hormone leads to too much IGF-1. And that can cause acromegaly symptoms and complications.
Risk Factors
People who have a rare genetic condition called multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 1 have a higher risk of acromegaly. This condition also is called MEN 1. In MEN 1, the parathyroid glands, pancreas and pituitary gland may grow tumors and release extra hormones. Extra parathyroid hormone can cause thin bones and kidney stones. A pancreas tumor may make the hormone insulin and cause low blood sugar. If the pituitary tumor makes extra growth hormone, acromegaly results. Very rarely, acromegaly can run in families.
When to see a Doctor
Get a healthcare checkup if you think you have symptoms of acromegaly. The condition usually develops slowly. Even family members may take a long time to notice the physical changes that happen. But it’s important for a healthcare professional to find the condition as early as possible. Treatment can help prevent serious health conditions that can happen along with acromegaly.
