COVID-19
What is COVID-19 ?
COVID-19, also called coronavirus disease 2019, is an illness caused by a virus. The virus is called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, or more commonly, SARS-CoV-2. It started spreading at the end of 2019 and became a pandemic disease in 2020. The virus that causes COVID-19 spreads most commonly through the air in tiny droplets of fluid between people in close contact. Many people with COVID-19 have no symptoms or mild illness. But for older adults and people with certain medical conditions, COVID-19 can lead to the need for care in the hospital or death.
Staying up to date on your COVID-19 vaccine helps prevent serious illness, the need for hospital care due to COVID-19 and death from COVID-19. Other ways that may help prevent the spread of this coronavirus includes good indoor air flow, physical distancing, wearing a mask in the right setting and good hygiene. Medicine can limit the seriousness of the viral infection. Most people recover without long-term effects, but some people have symptoms that continue for months.
Symptoms
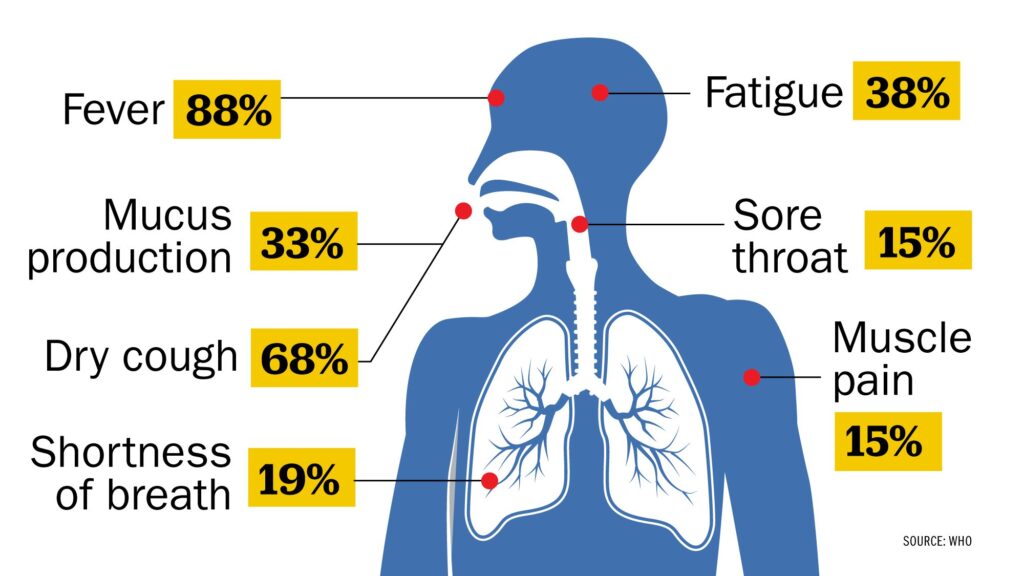
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Body aches
- Digestive problems
- Chills
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Loss or altered sense of smell, taste
- Difficulty thinking and focusing
Cause
COVID-19 is caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, also called SARS-CoV-2. The coronavirus spreads mainly from person to person, even from someone who is infected but has no symptoms. When people with COVID-19 cough, sneeze, breathe, sing or talk, their breath may be infected with the COVID-19 virus. The coronavirus carried by a person’s breath can land directly on the face of a nearby person, after a sneeze or cough, for example. The droplets or particles the infected person breathes out could possibly be breathed in by other people if they are close together or in areas with low air flow. And a person may touch a surface that has respiratory droplets and then touch their face with hands that have the coronavirus on them. It’s possible to get COVID-19 more than once. Over time, the body’s defense against the COVID-19 virus can fade. A person may be exposed to so much of the virus that it breaks through their immune defense. As a virus infects a group of people, the virus copies itself. During this process, the genetic code can randomly change in each copy. The changes are called mutations. If the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 changes in ways that make previous infections or vaccination less effective at preventing infection, people can get sick again.
Risk Factors
The main risk factors for COVID-19 are If someone you live with has COVID-19. If you spend time in places with poor air flow and a higher number of people when the virus is spreading. If you spend more than 30 minutes in close contact with someone who has COVID-19. Many factors affect your risk of catching the virus that causes COVID-19. How long you are in contact, if the space has good air flow and your activities all affect the risk. Also, if you or others wear masks, if someone has COVID-19 symptoms and how close you are affects your risk. Close contact includes sitting and talking next to one another, for example, or sharing a car or bedroom. It seems to be rare for people to catch the virus that causes COVID-19 from an infected surface. While the virus is shed in waste, called stool, COVID-19 infection from places such as a public bathroom is not common.
When to see a Doctor
If you have COVID-19 signs or symptoms or you’ve been in contact with someone diagnosed with COVID-19, contact your doctor or clinic right away for medical advice. Tell your health care team about your symptoms and possible exposure before you go to your appointment.
